Product Development Cycle Explained
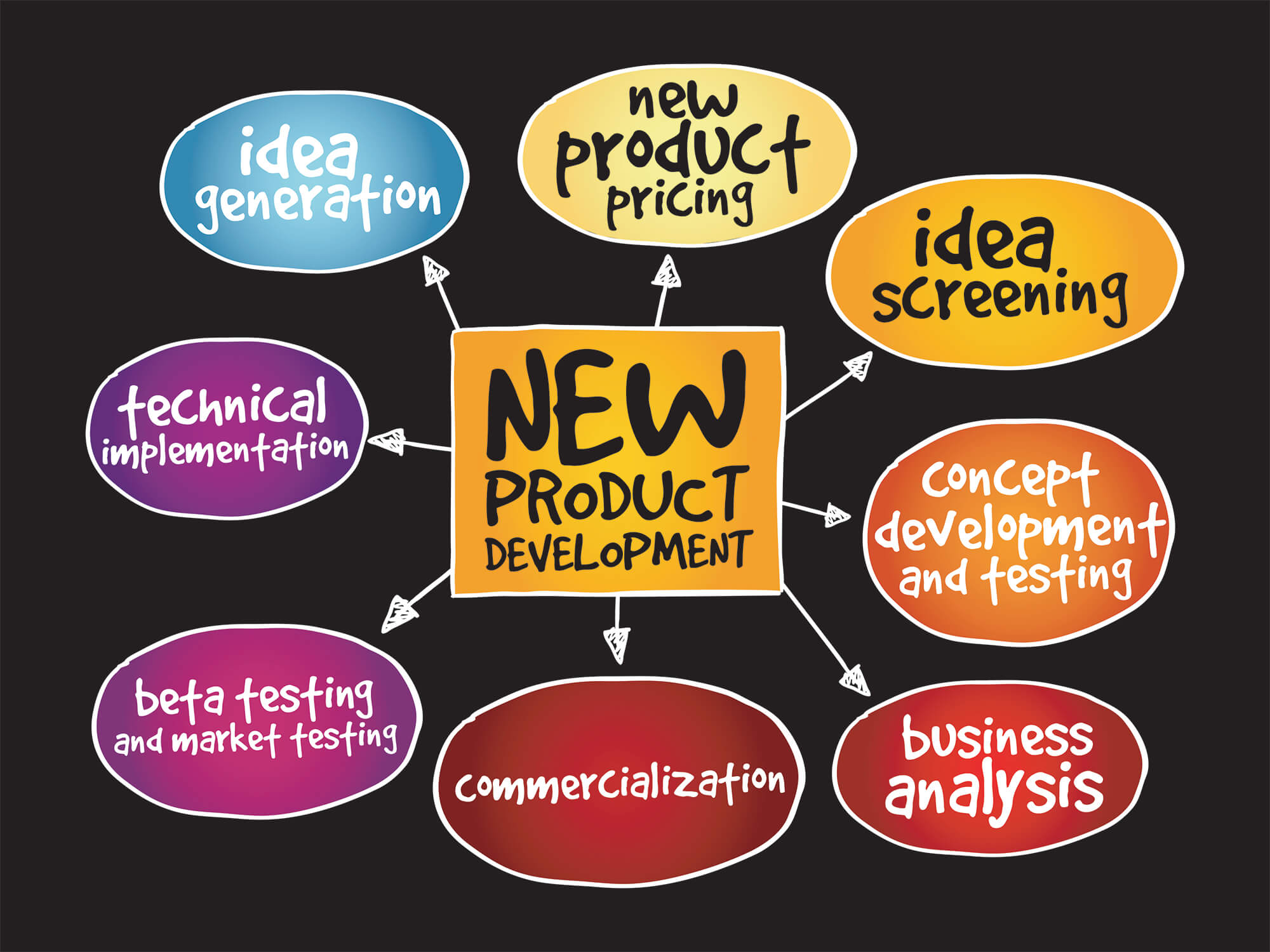
The product development cycle is a series of stages that a product goes through from its initial conception to its market launch and beyond. This cycle enables companies to transform a simple idea into a tangible product that meets the needs of its target customers. While the specific phases can vary by industry and product type, a typical product development cycle includes the following stages:
1. **Idea Generation:** This initial phase involves brainstorming and coming up with innovative ideas for new products. Ideas can come from various sources, including market research, customer feedback, competitor analysis, and internal innovation sessions.
2. **Concept Development and Screening:** In this stage, the feasibility of the ideas generated is evaluated. Concepts are assessed for their potential market demand, profitability, and alignment with the company’s goals and resources. This screening process helps in narrowing down the list to the most viable ideas.
3. **Design and Development:** Once a concept is selected, detailed planning, design, and development take place. This includes creating prototypes, developing the product design, and working out the technical specifications. It’s a critical phase where the conceptual product starts taking a tangible form.
4. **Testing:** The prototypes or initial versions of the product are subjected to various tests to evaluate their performance, safety, and reliability. Testing can include both internal assessments and user testing groups to gather feedback. This stage is crucial for identifying any issues or areas for improvement before mass production.
5. **Market Analysis and Business Analysis:** Concurrently with testing, detailed market analysis and business analysis are conducted. This involves studying the target market, setting pricing strategies, analyzing competitors, and forecasting sales. The goal is to understand the market dynamics and the product’s potential for success.
6. **Product Development and Refinement:** Based on feedback from the testing phase and market analysis, the product may undergo further development and refinement to address any issues or to better align it with market needs and expectations.
7. **Commercialization:** This final stage involves preparing for the product’s launch. This includes ramping up production, marketing and promotional activities, distribution planning, and sales strategy implementation. The product is officially introduced to the market, and the focus shifts to maximizing its reach and profitability.
8. **Post-launch Review and Lifecycle Management:** After the product is launched, it enters the lifecycle management phase. This involves monitoring its performance in the market, gathering customer feedback, and making necessary adjustments. Products may also evolve through additional features, updates, or improvements based on ongoing market demands and technological advancements.
Throughout the product development cycle, effective communication and collaboration among all stakeholders, including designers, engineers, marketing professionals, and financial analysts, are critical to a product’s success. Additionally, flexibility and responsiveness to feedback and market changes can significantly influence the outcome of the product development process.